Industrial Laser Marking Systems / Laser Markers
Laser Marking in the Aerospace Industry
-
Tags:
- Laser Annealing , Laser Engraving , Metal
Laser marking is a technology that is often used in the aerospace industry to engrave or mark components with great precision. It utilises laser beams to create permanent markings on various aerospace materials, ensuring traceability and compliance with industry standards.
Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Aerospace Part Marking Standards
The FAA is the government body behind deciding aerospace industry standards. In particular, the aerospace part marking standards. The FAA identified that marks must be visible and not have any interference with a part’s function. Accessible visibility allows for more efficient identification, recall, and shipments. Because of the importance of visibility, some parts include more than one mark for easier access to information.
It’s important to note that a component having a regulatory mark does not necessarily mean that the component or aircraft is acceptable to fly, so even if a part is in maintenance, it needs a mark.
That being said, every aircraft must have markings on every component before being installed. Let’s explore the aerospace laser marking requirements.
Aerospace Part Marking Standards Identification Requirements
- Builders name
- Model designation
- Builder’s serial number
- Type certificate (if applicable)
- Production certificate (if applicable)
- Established rating (if applicable)
Since all of this information is required, manufacturers usually use data matrix 2D codes to store it all. The data matrix code follows the ISO/IEC 106022:2006 standard so it’s scannable to reveal this information. Not only is a data matrix code helpful because it consolidates the information, but it also assists with easier data management and communication.
Aerospace Part Marking Standards for Aircraft Components
Aircraft components listed below must have marks that sustain normal air use, damage to the aircraft, or damage to the mark:
- Engines
- Propellers
- Propeller blades
- Propeller hubs
- Power parachutes
- Weight shift control aircraft
Aerospace Part Marking Standards for Aircraft
Aircrafts listed below must have marks that sustain normal air use and are legible from the ground:
- Manned free balloons
- Aircrafts made before March 7, 1988
- Power parachutes
- Weight shift control aircraft
Materials Used in the Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry mostly uses molten metal for forming die-cast components (the skeleton of the aircraft). The most popular molten metal for die-cast components is aluminium alloy. However, other alloys like zinc, magnesium, and copper are also used.
Aluminium Alloy in the Aerospace Industry
Aluminium alloy is particularly popular in the aerospace industry for many reasons:
- High thermal conductivity
- High electrical conductivity
- High corrosion resistance
- High strength
- Low cost
- High recycling ability
- Light-weight
- Dimensional stability
- Ability to form complex shapes
- High production rates
Aluminium Alloy Marking Challenges
Although aluminium alloys have many benefits as die-cast components, they can present challenges for many conventional marking methods. Among these, are susceptibility to deformities. The low hardness and high thermal expansion mean that aluminium alloys are sensitive to marking methods with heat or added force. Aluminium will physically deform with too much heat or force.
Being that the aerospace industry as a whole requires adherence to very tight tolerances, any marking technology that provides an opportunity for physical deformation or a change in mechanical properties can spell out disaster.
This sensitivity is why aerospace laser marking is the preferred method. Generally being a non-contact style of marking without excess heat stress, laser markers prevent many of these issues from arising.
Laser Marking Aluminium: Aerospace Laser Marking Solution
Incorporating lasers into aerospace part marking, especially on aluminium die-cast components, helps ensure compliance with aerospace part marking standards.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!
Aerospace Laser Marking Process
The aerospace laser marking process uses a focused laser beam to engrave, mark, or etch onto a component or an aircraft. The laser will either migrate, melt, or evaporate the material, leaving behind a clean mark made from the original material. It causes no harm to the part.
Carbon Migration Laser Marking
Carbon migration is a style of laser marking that is extremely popular in the aerospace industry as it leaves behind a mark that is highly contrasting and easy to see but does not raise the surface of the material or create any depth, thus allowing parts to still meet tight surface finish specifications and tolerances. The high contrast is particularly useful for data matrix codes.
This is achieved by de-focusing the laser to spread the heat over a wider beam spot. This act pulls the carbon content of the material to the surface level, creating a visible black mark.
This marking style is achieved only on ferrous materials. Ferrous materials are materials with iron content.
Laser Engraving
Laser engraving is a style of marking that creates an indented mark for aerospace laser marking. It works by shooting a focused laser beam onto the target, which heats it past the melting point and into vaporisation. Once the material evaporates, it leaves behind a clean, indented mark.
Unlike carbon migration, laser engraving is compatible with more than just ferrous materials. It’s possible to also engrave components made of aluminium or resin composite.
Laser Etching
Laser etching is a style of laser marking that creates a contrasted mark for aerospace part marking. This process works by shooting a focused beam onto the target, which then heats it to its melting point. The laser melts the target into a design, and the design solidifies into a contrasted mark.
Similar to engraving, laser etching also is possible on components made of resin composite.
Curious about our pricing?
Click here to find out more.
Benefits of Aerospace Laser Marking
Using a laser for aerospace part marking offers advantages, ensuring components stay within regulations. Laser marks are permanent, efficient, precise, damage-free, and environmentally friendly.
Permanent
Using a laser for aerospace part marking ensures permanent marks. There is no extra material like paper or ink that carries inherent risks like falling off or smudging.
Efficient
Laser marking and programme changeover can be done in seconds as opposed to hours of potential work. Laser marking for aerospace part marking combats supply chain bottlenecks and eliminates manual labour.
Precise
Laser marking uses micrometre precision for a perfect mark left behind.
Damage Free
Aerospace laser marking does not add friction or physically impact the component, which allows for a contactless form of marking.
Environmentally Friendly
Laser marking for aerospace part marking doesn’t use chemicals or extra consumables like ink or paper.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.
Aerospace Laser Marking Machine
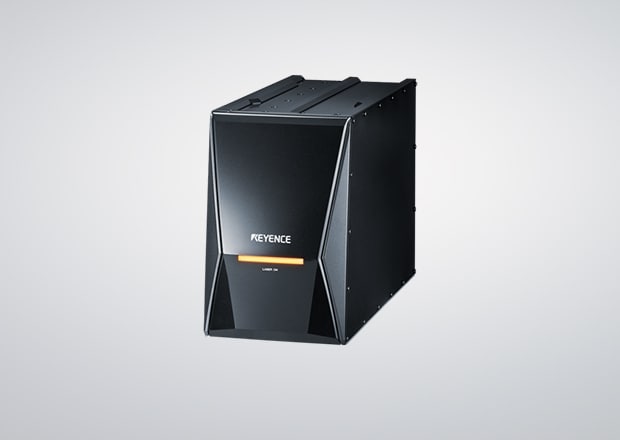

KEYENCE’s Hybrid Laser Marker MD-X Series
KEYENCE’s MD-X Series was designed to address many of the common concerns and challenges presented by tight tolerance manufacturing, such as what is seen in the aerospace industry. With industry-leading 3-Axis beam control and ultimate flexibility, the MD-X should be the top choice for aerospace laser marking.
MD-X Key Features
- Tilt Correction
-
MD-X uses Z tracking to account for large part tilts during mounting so that the marking is level and adjusts with the tilt. With the size, style, and importance of parts that the aerospace uses to assemble an aircraft, tilt correction is necessary.
- XY Tracking
-
The MD-X uses a built-in sensor and camera to track the positional and focal deviation of part targets. With XY Tracking, the laser adjusts based on positioning and recognises changes in part position and changes accordingly. Die-cast components can be deformed, and XY Tracking will align the mark to the position of the part or send a warning if the component is incorrect.
- Depth of Focus
-
The depth of focus creates high-contrast marks that are legible and fit aerospace part marking standards.
- 3-Axis Control
-
Unlike most laser machines with fixed focal points across a singular plane, KEYENCE lasers mark on the 3-Axis (X, Y, Z) plane. The ability of the beam to mark on these axes means there’s an ease of marking on complex or curved shapes. Unlike a single plane where markings become deformed when not marking on a flat surface, a 3-Axis controlled beam means that the mark curves with the component.
Since the mark aligns with natural curves, components like propellers, disks, engines, rings, and turbines can have readable data matrix codes. - 2D Code Reader
-
The MD-X Series lasers include a built-in 2D code reader. Instead of risking trial and error, the built-in 2D code reader assures the quality and readability of the code immediately after marking.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalogue.
View Catalogue
Looking to Incorporate Aerospace Laser Marking?
Aerospace laser marking is an efficient, precise, and permanent option for keeping your organisation up to aerospace part marking standards. If you’re ready to explore aerospace laser marking, we can help.
Choosing KEYENCE for aircraft part marking equipment means you’re getting more than just a standard laser. Our lasers are built for the needs of the aerospace industry with tilt correction, 3-axis control, and 2D code reader for prime readability regardless of your component’s shape.
At KEYENCE, our laser markers and knowledgeable staff are ready to consider your industry needs to give you the best marking results. Contact our team today for a free demo or to discuss further.
Curious about our pricing?
Click here to find out more.






