Industrial Laser Marking Systems / Laser Markers
Fibre Laser: Everything You Should Know
-
Tags:
- Laser Engraving , Metal , Laser Cleaning
There are many types of laser marking systems: UV, CO₂, YVO4, hybrid, green, and fibre laser. Each has specifications that make each more or less qualified to tackle different processing tasks. Because of this, many questions may arise, such as:
- What makes a fibre laser special, and in what case should you choose it over the others?
- What is a fibre laser?
- How does a fibre laser work?
What is a Fibre Laser?
A fibre laser is a solid-state laser known for a 1090 nm wavelength and high output power. Thanks to the incredibly high heat generated by the laser, it can easily and efficiently cut, engrave, mark, etch, and remove burrs from materials. Fibre lasers boast rapid production speed because of their high output and high heat. Not only that, these two features make fibre lasers the best option for metal processing.
How Does a Fibre Laser Work?
A fibre laser works by using an optical fibre as a resonator to amplify the laser beam. This is done by producing an overlapping structure of fibre cladding doped with Yb ions. A laser diode excitation is then pumped inside the fibre to generate a high-output laser. In turn, the laser is optimal for deep engraving, annealing, and cutting – especially for large production batches of repeated tasks that need quick completion.
However, due to the high output of heat produced by fibre lasers, they may not be the ideal choice for marking on non-metals. Some non-metals have very low melting points, meaning that fibre lasers could disrupt their structural integrity by melting beyond the target area. On the other hand, other non-metals have high melting points that combat the fibre's beam. With the high melting point, the fibre laser may not be able to achieve the preferred darkest mark. In these cases, alternative laser types may be a better option.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!
Top Industries That Use Fibre Lasers
Fibre lasers are extremely common in industries that involve the manufacturing of metal and metal components. These include but are not limited to:
- Semiconductor / LCD
- Aerospace
- Automobile
- Medical Technology
- Electronic Devices
- Metals
Different Applications for Fibre Lasers
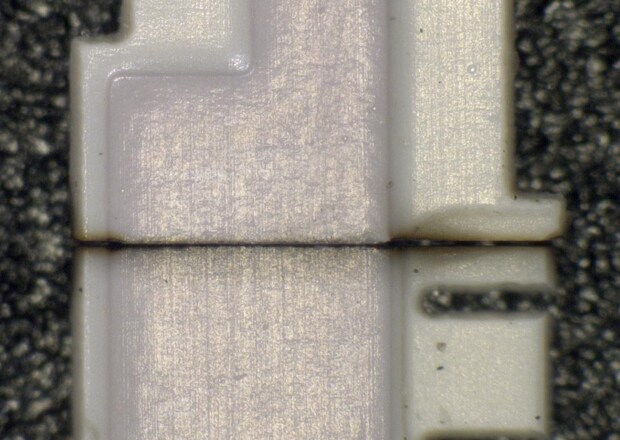
Deep Engraving
The main benefit of fibre lasers over other types of marking systems is the high-output power that they feature. Compared to other systems, a high-output fibre laser can lead to remarkable improvements in marking time, efficiency, engraving depth, and mark quality.
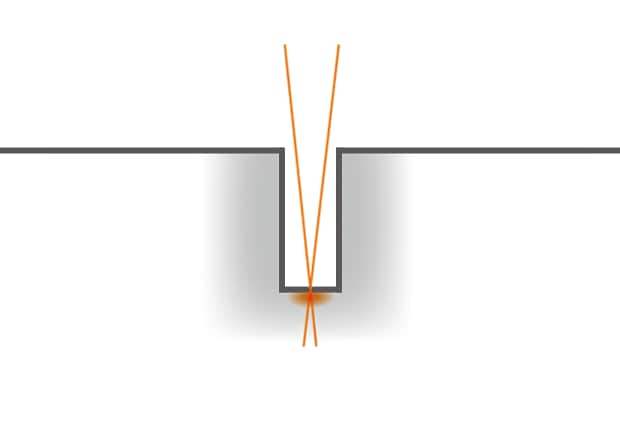
A common issue presented in these deep engraving applications is the focus of the laser. As engravings go deeper and deeper, the focal point of the engraving becomes further and further from the lens of the laser. This can present issues as an out-of-focus laser will dramatically reduce the amount of depth achievable.
This is another area where the 3-Axis design of KEYENCE's laser engravers stand tall against other solutions. Using the "Deep-Dig" function, the laser's software can account for the varying focal depth due to engraving and automatically adjust the focal distance of the laser beam. This means that as the engraving gets deeper and deeper, KEYENCE lasers will never lose focus resulting in deeper, faster, cleaner engravings.
Walk into any automotive manufacturing facility, and you are likely to see a fibre laser engraving traceability marking on engine or drivetrain components.
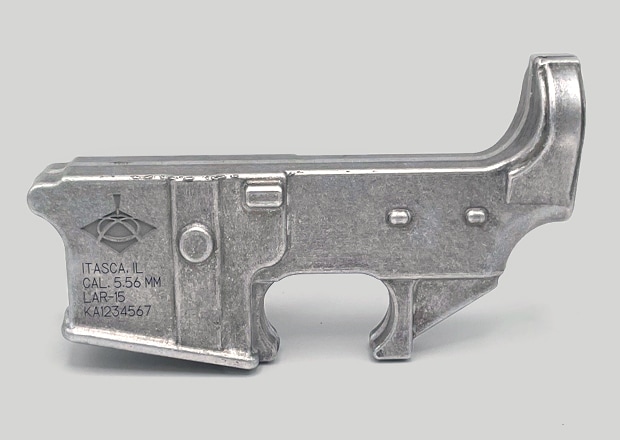

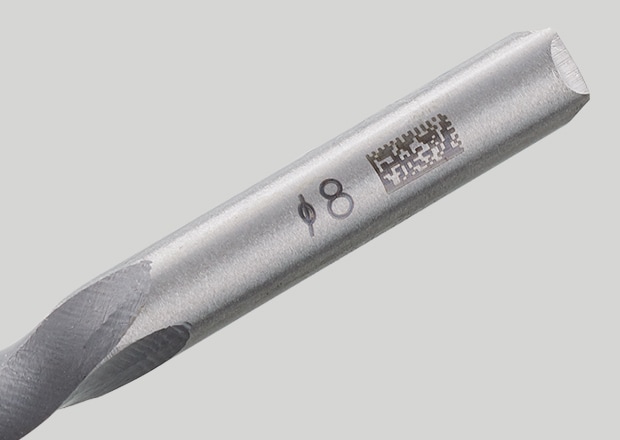
Black Annealed Marking
Black annealed marking is the process of applying a laser beam to a target and then shifting the focus so only heat is conducted. The laser does not engrave but rather forms an oxide film on the surface that appears as a black mark but cannot be felt to the touch.
KEYENCE fibre lasers are effective for anneal-style marking as they offer 3-axis beam control. This allows the laser to automatically adjust the focus of the laser to spread the beam spot over a wider area. This is instrumental in ensuring a high-contrast anneal, without damaging the surface of the workpiece.
Black annealed marking is used on metals like titanium, stainless steel, and iron alloys and is extremely common in both the medical and aerospace industries as it can provide a fully permanent mark with little to no damage to the surface it is marked on.


Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is done by focusing the laser light output by a laser oscillator and irradiating any fixed point from the irradiation unit to melt the target. Since the fibre laser uses high output power, the fibre laser excels at laser cutting because of the quick melting of the material. With quick melting, the material is cut instantly without any effect on the rest of the material. When cutting with a fibre laser, a range of materials—from metals to plastic—can be cut by a fibre laser.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.
How Can a Fibre Laser Help Your Particular Needs?
Industry, material, or the speedy factor of fibre lasers resonate with you? If you're looking for a versatile, fast, and high-output laser that can achieve annealing, deep engraving, cutting, burr removal, etching, or any kind of permanent marking on metal or plastic components, then a fibre laser may be right for you. Contact KEYENCE today for a free demo to see how a fibre laser can optimise your production needs!
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us