Colour Resolution
Colour resolution refers to the ability of each pixel to represent a number of colour tones (also called colour depth or bit depth).
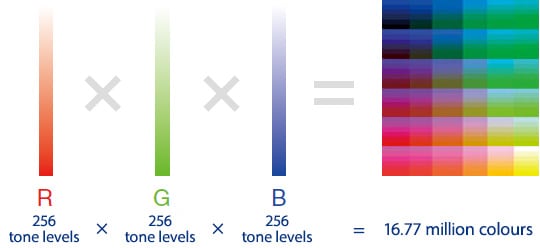
Colour resolution is normally measured by the level of ability to express the intensity of the 3 primary colours (red, green, and blue).
The number of levels available to represent each colour depends on the number of bits that can be used to uniquely characterise each shade.
For example, when using an 8-bit colour camera, each individual colour has 8 bits or 256 levels (2 to the 8th power) to represent its range.
When evaluating the primary colours (R,G,B), an 8-bit colour camera can render 16,777,216 colours (256 × 256 × 256).
On average, it is said that the human eye can differentiate between approximately 10 million colours.
Thus, the representation of 16.77 million colours should be more than enough.
However, in reality, the ability of the human eye to analyse colours differs depending on the colour being viewed (e.g. human eyes have a high sensitivity to green).