Image Capture and Analysis of Flexography Using a Digital Microscope
We encounter printing everywhere, on food and medicine packages, books, magazines, and many other items.
This section introduces examples of image capture and analysis of flexography using our digital microscope.

- What Is Flexography? (Featuring Intensity and Beauty of Printed Characters)
- Examples of Image Capture and Analysis of Flexography Using a Digital Microscope
What Is Flexography? (Featuring Intensity and Beauty of Printed Characters)
Flexography is a form of relief printing. A relief printing plate is a plate with non-recessed surfaces that transfer characters and pictures.
Printing is performed by applying ink to the non-recessed surfaces, just like block printing and stamping.

- A: Anilox roller
- B: Doctor blade
- C. Ink
- D: Plate
- D: Plate cylinder
- F: Impression cylinder
- G: Printing paper
In flexography, ink is applied to non-recessed resin surfaces via the anilox roller and then transferred to printing paper.
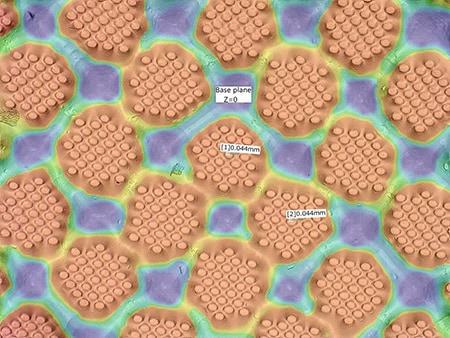
Gradation in images such as photographs is expressed using halftone dots, which are tiny dots, because it is impossible to use different inks according to the gradation, such as using dark ink for dark areas.
Relief printing uses small amounts of ink and is excellent for reproducing tiny characters and sharp depiction. It is also suitable for printing on products with low smoothness such as cardboard and paper bags.
Examples of Image Capture and Analysis of Flexography Using a Digital Microscope
This section introduces the latest examples of image capture and analysis of flexography using KEYENCE’s VHX Series 4K digital microscope.